2026 How to Master Robotic Grinding Techniques for Industrial Applications?
In the evolving landscape of industrial manufacturing, robotic grinding has emerged as a game-changer. This technique improves precision and efficiency in various applications. However, mastering robotic grinding requires a nuanced understanding of technology and process.
Many industries are adopting robotic systems for grinding tasks. These systems offer consistent results, reducing human error. Yet, challenges remain. Workers need to learn new skills. It can be difficult to adapt to robotic systems. Individuals may struggle with programming and maintenance. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution.
Moreover, different materials present unique challenges. Certain metals require specific techniques to avoid damage. Understanding this is crucial for success. Companies that invest time and effort in training will see the best results. Yet, training programs often lack depth. It’s essential to critically evaluate these programs. The goal is to create a workforce that thrives in this robotic era.
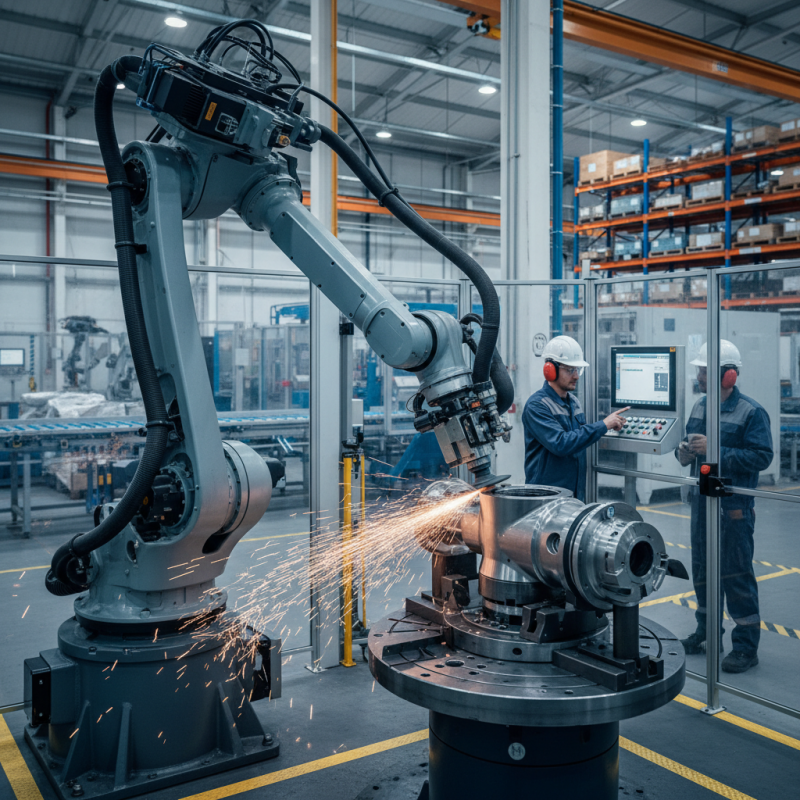

Understanding the Basics of Robotic Grinding in Industrial Settings
Robotic grinding is becoming essential in modern manufacturing. It enhances precision and efficiency. Understanding the basics of robotic grinding is crucial for successful implementation.
In various industrial settings, grinding is used for removing material. This process shapes parts to desired specifications. Choosing the right automation technique is vital. Factors impacting choice include the material type, part geometry, and production volume. Each element can make a significant difference in outcomes.
**Tip:** Invest time in training operators. Knowledgeable staff can optimize robot programming. This reduces the chances of errors and increases output quality.
Common mistakes often occur in setup and calibration. These can lead to subpar results. Regular checks on equipment can help avoid these pitfalls. Keeping an eye on wear and tear is equally important.
**Tip:** Schedule routine maintenance for all robotic systems. This ensures consistent performance and longevity. Small issues, if ignored, can escalate into major problems.
Robotic grinding may seem straightforward, but it requires attention. Continuous learning and adaptation are necessary for success. Embracing these challenges will lead to improved productivity over time.
Key Technologies Driving Robotic Grinding Solutions Today
The landscape of robotic grinding is evolving rapidly. Key technologies are shaping how industries approach grinding tasks. For instance, machine vision systems enhance precision by enabling robots to identify parts accurately. This capability is crucial in industries where tolerances are tight. According to a recent industry report, companies utilizing advanced robotic grinding solutions reported a 30% reduction in production time.
Another important technology is the integration of artificial intelligence. AI algorithms can learn from past grinding tasks and optimize processes for better efficiency. This not only boosts productivity but also reduces wear and tear on grinding materials. An analysis revealed that firms applying AI saw a 25% decrease in operational costs. Yet, many organizations still struggle with adopting these technologies fully. There remains a gap between understanding these benefits and implementing them effectively.
Furthermore, safety is a persistent concern. While robotic systems can improve worker safety, improper integration can lead to accidents. It is essential for companies to invest in training and ensure their workforce understands how to work alongside these systems. The potential for error is a real challenge that needs addressing. Balancing innovation with safety is crucial for industry success.
Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing the Right Robot for Grinding Tasks
When selecting a robot for grinding tasks, several key factors must be considered. First, the robot's payload capacity is crucial. A report from Robotics Industry Association notes that the right payload can significantly impact efficiency. Robots often come with different payload limits, which directly affect their grinding capabilities. For materials like metals, ensuring that the robot can handle the weight is essential for sustained performance.
Next, consider the grinding application itself. Task complexity varies greatly across industries. In automotive manufacturing, for example, specialized robots perform intricate grinding on engine components. According to a study by MarketsandMarkets, automated grinding solutions can enhance productivity by up to 40%. However, this efficiency comes with challenges. Operators may face learning curves in programming these advanced models. It's vital to evaluate not just technical specifications, but also ease of integration into existing systems.
Finally, automation level matters. Robots can vary from semi-autonomous to fully autonomous models. A McKinsey report indicates that more than 60% of tasks in manufacturing can be automated. Yet, transitioning to full automation is not always seamless. Some companies may struggle with maintaining quality control after implementing robotic solutions. The process requires reflection and adjustment over time, ensuring the chosen robot continues to meet production standards.
Techniques for Programming Robots for Efficient Grinding Operations
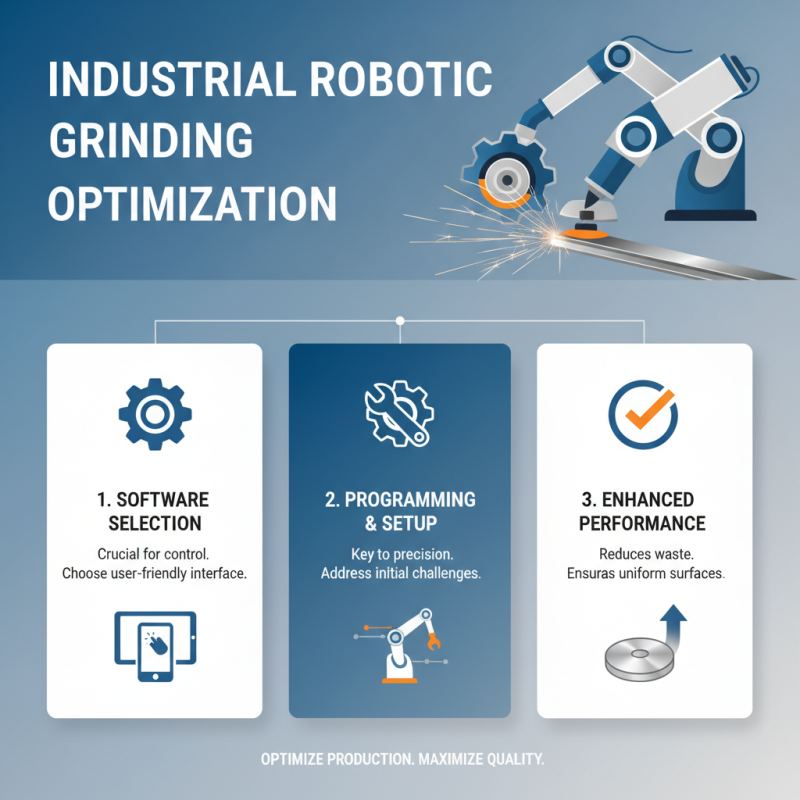
Robotic grinding is becoming essential in industrial applications. Programming robots effectively can significantly enhance grinding operations. The first step involves selecting the right software interface to guide the robots. Many users find the initial setup challenging, often leading to misalignments. This can result in uneven surfaces and wasted material.
Once the programming interface is in place, focus shifts to the robot's path planning. Defining the optimal path is crucial. Too often, operators neglect this and end up with subpar results. Careful analysis is necessary to identify all potential issues. Effective programming requires continuous testing and adjustments. Small tweaks can lead to major improvements.
Feedback loops are invaluable during the grinding process. Monitoring the robot's performance in real-time allows for quick corrections. Operators may struggle with understanding data outputs. They tend to overlook this critical aspect. Iterative learning and adaptation enhance grinding precision. The goal is to minimize waste while maximizing efficiency.
Best Practices for Maintenance and Troubleshooting in Robotic Grinding
Robotic grinding techniques are increasingly vital in industrial settings. However, maintenance and troubleshooting remain significant challenges. Data shows that improper maintenance can lead to a 10% reduction in efficiency and increase operational costs.
Regular inspections of robotic grinding systems are essential. Check for wear in grinding wheels and monitor motor temperatures. Overheating can signal potential failures. Industry reports estimate that 70% of machinery breakdowns stem from insufficient upkeep. Don't hesitate to replace worn parts promptly.
Troubleshooting can be tricky. Many operators fixate solely on visible issues. But often, it's the unseen problems that cause downtime. For instance, if a robot struggles with precision, it might not be due to the grinder itself. Calibration errors can arise from misaligned sensors or software glitches. These require thorough checks and adjustments. Remember, a holistic approach to maintenance can prevent costly repairs and keep production running smoothly.
Related Posts
-

Exploring the Future: Top Robotic Systems to Watch in 2025
-

What is a Robotics Technician? Skills, Responsibilities, and Career Path Explained
-

How to Start Successful Robotics Projects for Beginners in 2025
-

How to Choose the Best Robotic Solutions for Your Business?
-

Why Robotic Process Automation is Transforming Business Efficiency Today?
-
Top Benefits of Robotic Automation for Businesses in 2023
