What is a Robotic Welding Cell? Benefits, Uses, and Applications Explained
In recent years, the adoption of robotic welding cells has surged across various industries, marking a significant shift towards automation in manufacturing processes. A robotic welding cell equips facilities with the ability to enhance efficiency and precision in welding operations. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global robotic welding market is projected to reach $6.9 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 11.2% from 2019 to 2026. This growth underscores the increasing reliance on automated solutions to meet rising production demands and improve overall quality.
Robotic welding cells are highly versatile and can be employed in multiple applications, from automotive manufacturing to construction. The integration of robotics aids in reducing labor costs while also minimizing weld defects, resulting in a significant return on investment for manufacturers. According to a survey by the Robotic Industries Association, companies that implement robotic welding report up to a 30% improvement in operational efficiency and a 50% reduction in rework due to enhanced welding accuracy. Thus, understanding the benefits and diverse uses of robotic welding cells is crucial for businesses aiming to remain competitive in an evolving marketplace.
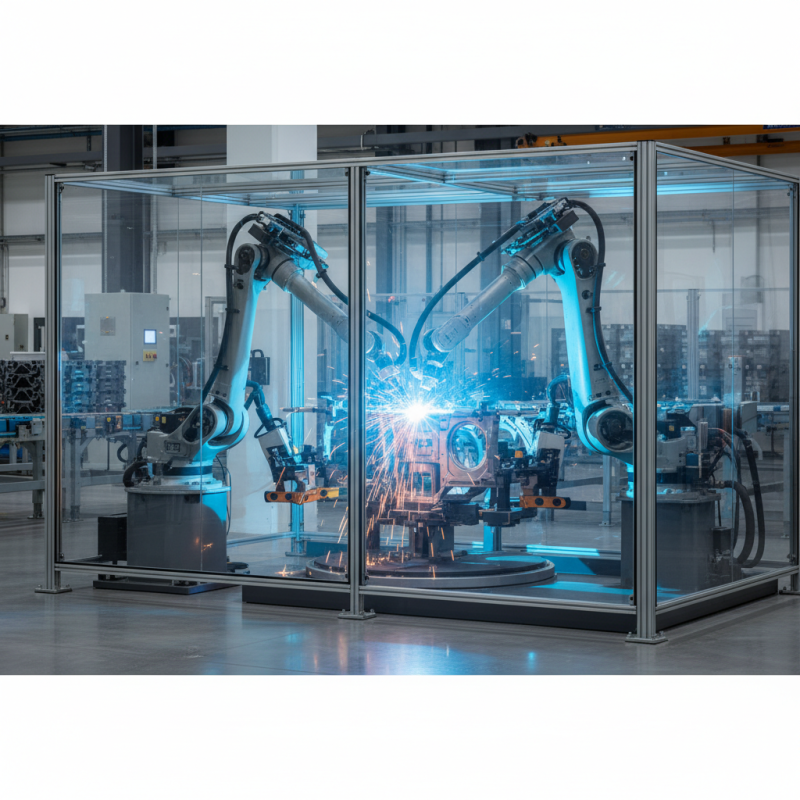

What is a Robotic Welding Cell?
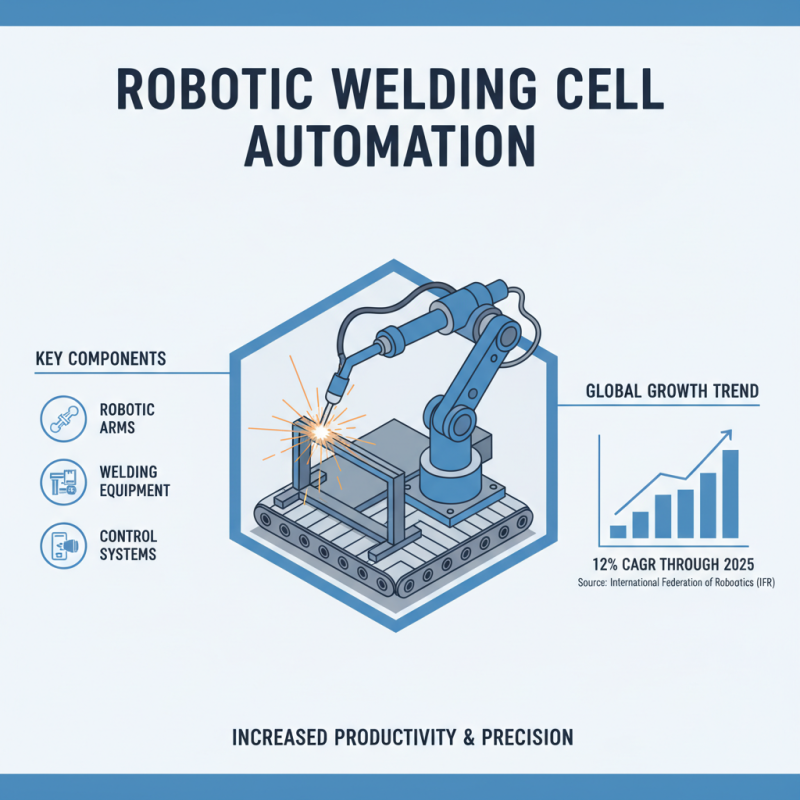
A robotic welding cell is a highly automated environment designed specifically for welding processes using robotic systems. These cells integrate various components, including robotic arms, welding equipment, and control systems, to facilitate efficient welding operations. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, the adoption of robotic welding has surged, with estimates suggesting that the sector will grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12% through 2025. This growth is driven by advancements in technology and the need for increased productivity and precision in manufacturing processes.
The use of robotic welding cells offers numerous advantages, such as enhanced efficiency, reduced operational costs, and improved weld quality. These systems can operate continuously with minimal human intervention, leading to significant reductions in cycle time. Furthermore, robotic cells can achieve high levels of consistency, which is crucial in industries such as automotive and aerospace where precision is paramount. A report from MarketsandMarkets indicates that the global robotic welding market is projected to reach $4.9 billion by 2025, highlighting its critical role in modern manufacturing.
Tips: When considering the implementation of a robotic welding cell, assess the specific needs of your production line and evaluate the total cost of ownership, including maintenance and training. Additionally, regularly updating software and hardware components can enhance the overall efficiency and adaptability of the system, ensuring it remains competitive in a rapidly evolving industry.
Key Components of a Robotic Welding Cell
A robotic welding cell is a sophisticated system that integrates various components to automate the welding process, enhancing precision, efficiency, and safety in industrial applications. The key elements of a robotic welding cell include the robotic arm, welding power source, control system, workpiece positioning devices, and safety equipment. The robotic arm, often equipped with various welding tools, is engineered to perform complex welds with a high level of accuracy. Research indicates that the incorporation of robotic systems can improve productivity by up to 30% compared to manual welding techniques.
The welding power source is essential in providing the necessary energy to perform the welding tasks. Advanced power sources can adapt to different welding methods, such as MIG and TIG, ensuring high-quality joints. The control system, typically utilizing sophisticated software, coordinates the robotic arm's movements and the welding parameters, allowing for seamless operation. Additionally, workpiece positioning devices play a critical role in ensuring that components are held securely in place during welding, which minimizes errors and improves overall weld integrity. Safety equipment, mandatory in any automated system, protects workers from potential hazards associated with welding operations.
According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, the global adoption of industrial robots, including robotic welding cells, is projected to grow by 12% annually. This trend highlights the increasing reliance on automation in manufacturing sectors, emphasizing the importance of these key components in enhancing operational efficiency and maintaining high production standards.
Benefits of Implementing Robotic Welding Cells
Implementing robotic welding cells offers numerous advantages that can significantly enhance production efficiency and quality in manufacturing environments. One of the primary benefits is the consistency in weld quality. Unlike human welders, robots operate with precision, performing repetitive tasks without fatigue, which leads to uniform welds and reduced variability. This reliability not only improves the overall quality of the products but also minimizes the need for rework, resulting in lower production costs.
Another major benefit of robotic welding cells is the increased safety they bring to the workspace. Welding is inherently hazardous, with risks of burns, exposure to harmful fumes, and other workplace injuries. By automating the welding process, robotic cells can significantly reduce human exposure to these dangers, creating a safer work environment. Furthermore, the ergonomic design of robotic systems limits the need for manual handling of heavy materials, further protecting workers from injury.
Additionally, the flexibility of robotic welding cells enables manufacturers to adapt quickly to changes in production demands. With the ability to program different welding tasks, companies can easily switch between various components and products without extensive downtime. This agility is crucial in today’s market, where customization and rapid response are key to staying competitive. Overall, the implementation of robotic welding cells not only boosts productivity but also enhances workplace safety and operational flexibility.
What is a Robotic Welding Cell? Benefits, Uses, and Applications Explained
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Automation Level | High - reduces manual labor and human error |
| Production Speed | Increased efficiency with faster cycle times |
| Precision | Consistent weld quality with high accuracy |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to various welding processes and materials |
| Safety | Reduces worker exposure to hazardous environments |
| Cost Savings | Lower labor costs and reduced material waste |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, construction, and manufacturing |
Common Uses of Robotic Welding in Industries
Robotic welding has become an integral part of various industries, thanks to its efficiency and precision. In the automotive sector, robotic welding cells are extensively used for assembling vehicle frames and components. These systems are capable of performing repetitive tasks at high speeds, which significantly reduces production time and enhances overall output. Moreover, the consistency achieved through robotic welding is vital for ensuring the safety and durability of automotive structures, leading to a higher quality final product.
In addition to automotive, robotic welding finds applications in manufacturing sectors such as aerospace, construction, and consumer goods. In the aerospace industry, precision welding is crucial for creating lightweight and strong structures that can withstand extreme conditions. Robotic systems facilitate the complex welding processes required for various components, ensuring high standards of quality and safety. Similarly, in construction, robotic welding streamlines the fabrication of metal structures, improving both efficiency and accuracy. These applications illustrate how robotic welding technology can significantly improve productivity and output quality across diverse industries.
Future Trends and Innovations in Robotic Welding Technology
The future of robotic welding technology is poised for significant advancements, driven by developments in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and automation. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global robotic welding market is expected to reach $6.5 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 10.3% from 2021. This surge is attributed to the increasing demand for precision and efficiency in manufacturing processes. Industries such as automotive and aerospace are leading the charge, leveraging robotic welding cells to achieve enhanced productivity and lower operational costs.
Moreover, the integration of real-time data analytics and IoT capabilities into robotic welding systems is transforming the manufacturing landscape. These innovations enable manufacturers to monitor performance metrics and make data-driven decisions, optimizing workflows and minimizing downtime. A study by Grand View Research highlights that the anticipated rise in automation in manufacturing may result in reduced labor costs by up to 20%, further emphasizing the economic benefits of adopting robotic welding technologies. As these systems become more sophisticated and user-friendly, the potential for broader applications across different sectors, including construction and electronics, is on the horizon, promising a future where robotic welding is a staple in industrial operations.
Related Posts
-

Revolutionizing Manufacturing: The Impact of Automated Welding Cells on Production Efficiency
-
2025 Top 10 Robotic Welding Automation Trends You Need to Know
-

Maximizing Efficiency in Manufacturing with Advanced Robotic Welding Systems and Their Impact on Production Rates
-

The Future of Manufacturing Embracing Robotic Welding Systems and Their Impact on Industry
-

How to Choose the Right Robotic Welding Cell for Your Manufacturing Needs
-

2025 Top 5 Automated Welding Robots Revolutionizing Efficiency with 30% Productivity Increase
