What is Robotic Welding Systems and How Do They Work?
In the rapidly evolving world of manufacturing, robotic welding systems have emerged as a game changer. According to Dr. Emily Chen, an expert in automation, “Robotic welding systems are redefining efficiency and precision in the industry.” These systems utilize advanced technology to automate the welding process, providing consistent quality and reducing labor costs.
Robotic welding systems integrate various components, including robots, controllers, and welding equipment. They work by programming the robot to perform precise welding tasks, which can lead to improved output and less waste. However, not all manufacturers fully embrace this technology. Some express concerns about the initial investment and the learning curve involved in integrating these systems.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of robotic welding systems are hard to ignore. They enhance productivity and can improve safety in the workplace. As industries continue to explore automation, the importance of understanding robotic welding systems will only grow. The journey to harness their full potential offers much for teams to reflect upon and improve.
Definition of Robotic Welding Systems
Robotic welding systems are automated machines designed for welding tasks. These systems can handle various types of welding, including MIG, TIG, and spot welding. They often consist of a robotic arm, welding equipment, and sensors. According to a report from the International Federation of Robotics, the automotive industry extensively employs robotic welding, accounting for about 30% of all robotic installations worldwide.
These systems offer significant advantages over manual welding. They ensure consistent quality and reduce human error. A study showed that factories using robotic welding saw a 30% increase in production efficiency. Robots can work in hazardous environments, which protects human workers from injuries. Additionally, robotic systems can operate 24/7, leading to higher output rates.
Tips: When implementing robotic welding, it's essential to assess the workspace layout. Some areas may not be suitable for robots. Consider training staff on system operation and maintenance, even for automated systems. Regular checks on system performance can prevent unexpected downtime. It's crucial to stay updated with industry advancements, as technology evolves rapidly. This can enhance workflow and productivity in the long run.
Key Components of Robotic Welding Systems
Robotic welding systems are complex but fascinating. They consist of several key components, each crucial to their operation. One of the main parts is the robotic arm. This arm is highly articulated, allowing it to maneuver precisely. It moves seamlessly in three-dimensional space, which is vital for accurate welding.
Another essential component is the welding machine itself. This machine generates the heat needed for the welding process. It can use different techniques, like MIG or TIG welding. These methods vary in their use of filler materials and the nature of the welds they produce. There may be times when the weld quality is less than expected. This requires operators to assess the parameters carefully.
Additionally, there are sensors integrated into the system. These sensors ensure that the robotic arm is positioned correctly. They detect any misalignment that could lead to defects. However, relying solely on technology can sometimes introduce errors. Regular maintenance and manual checks are necessary to mitigate this risk. Automation is powerful, but human oversight remains critical.
Robotic Welding Systems: Efficiency Comparison by Application
Working Principle of Robotic Welding Systems
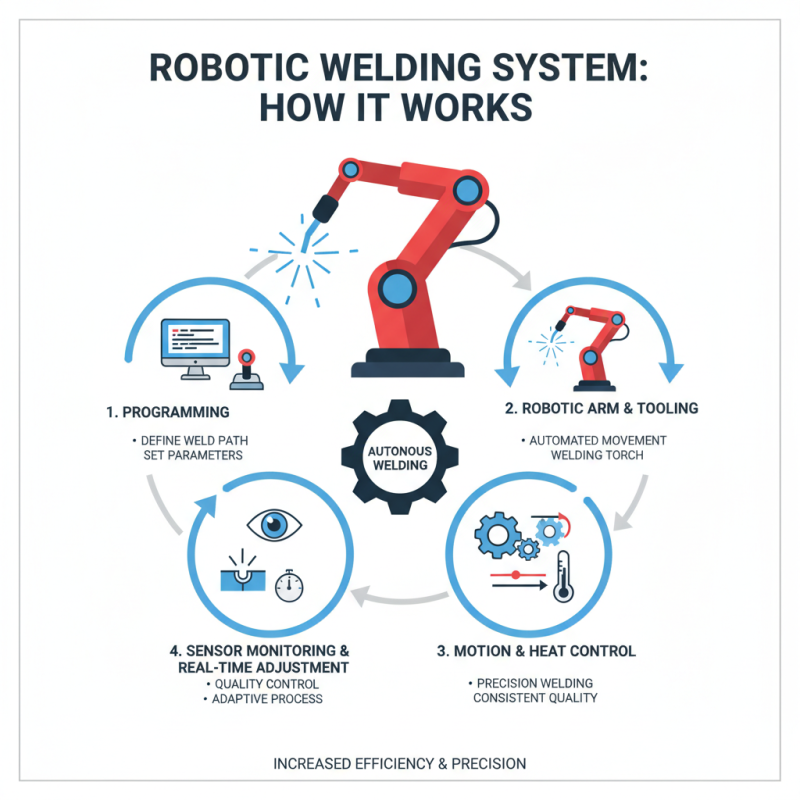
Robotic welding systems operate through a combination of sophisticated technology and programming. These systems use robotic arms equipped with welding tools to perform welding tasks autonomously. The working principle revolves around the precise control of motion and heat application. Sensors are integrated to monitor the welding process and adjust parameters in real time, ensuring quality and consistency.
Research indicates that companies implementing robotic welding can achieve up to 30% improvement in productivity. Additionally, they often experience reduced operational costs and minimized human error. However, integrating these systems requires initial investment and training. Many companies face challenges in seamlessly transitioning from manual to robotic processes.
Improvement through robotic welding is not without its flaws. Misalignment or incorrect settings can lead to defects, impacting product quality. Continuous feedback and adjustments are necessary to maintain optimal performance. According to industry reports, about 15% of robotic welding tasks may still require human oversight to address complexities. Understanding these limitations is essential for businesses considering automation in their welding operations.
Applications of Robotic Welding in Various Industries
Robotic welding systems have transformed various industries by enhancing efficiency and precision. In automotive manufacturing, for instance, about 90% of all vehicles produced utilize robotic welding. This technology ensures uniformity, which is crucial for safety standards. It also minimizes human error, leading to fewer defects.
In the aerospace sector, robotic welding plays a vital role. Complex structures require high precision. According to industry reports, automation in aerospace welding can reduce production time by up to 30%. However, transitioning to these systems can be costly and requires skilled technicians to troubleshoot when issues arise. Moreover, the learning curve can hinder new adopters.
The construction industry is also seeing an increase in robotic welding applications. Robots handle repetitive tasks, allowing skilled labor to focus on more complex work. Yet, the reliance on automation raises concerns about job displacement. Companies must find a balance between efficiency and workforce impact, fostering upskilling and training programs to address this reality.
What is Robotic Welding Systems and How Do They Work? - Applications of Robotic Welding in Various Industries
| Industry | Common Applications | Advantages of Robotic Welding | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Frame assembly, Body welding | High precision, Increased speed | Initial setup cost, Training required |
| Construction | Steel structure assembly | Improved safety, Reduction in manual labor | Complex programming, Site mobility issues |
| Shipbuilding | Hull construction, Pipe welding | Consistency, Long weld runs | Environmental factors, Equipment reliability |
| Aerospace | Component assembly, Tank welding | Reduced weight, Enhanced quality control | Regulatory compliance, High precision requirements |
| Manufacturing | Product assembly lines | Increased productivity, Reduced operational costs | Maintenance needs, Software updates |
Advantages and Challenges of Using Robotic Welding Systems
Robotic welding systems have transformed the manufacturing landscape. They offer precision and speed. However, there are both advantages and challenges to consider.
One major advantage is consistency. Robots can weld with the same quality repeatedly. This reduces human error. Welds are often stronger and more uniform. Additionally, they can operate in hazardous environments, keeping human workers safe. This aspect is crucial in industries such as
automotive and construction.
On the flip side, challenges arise. Initial setup costs can be high. Training staff to work alongside robots is essential. Maintenance of the systems can also be intricate. There may be downtime due to repairs, which disrupts production. Companies must weigh these factors carefully. Decision-making shouldn't be rushed. Each scenario is unique, and the impact on workflow must be considered.
Related Posts
-

The Future of Manufacturing How Robotic Welding Machines Are Revolutionizing the Industry
-

How to Choose the Right Robotic Welding Cell for Your Manufacturing Needs
-

Maximizing Efficiency in Manufacturing with Advanced Robotic Welding Systems and Their Impact on Production Rates
-

The Future of Manufacturing Embracing Robotic Welding Systems and Their Impact on Industry
-

Revolutionizing Manufacturing: The Impact of Automated Welding Cells on Production Efficiency
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Robotic Welding Machines in Modern Manufacturing
